Word VBA Symbols to Entities Conversion Program
Symbols when converted to Text (Save as Text) seldom retain the original shape. It has been a practice to convert these symbols to entities (mostly the symbol name prefixed with an ampersand and followed by a semi colon), for example, α † etc
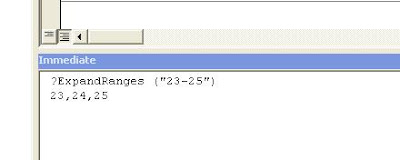
The following code expects a tab separated text file with symbol’s character code and its corresponding entity representation. For example
176 & degree;
945 & alpha;
To know about the corresponding character code for a symbol, you can use Alt + Symbol Key. For example Alt + 0151 will give an emdash etc
Or you can check from Insert -- > Symbol
 Word Insert Symbol Dialog
Word Insert Symbol Dialog
We read the text file using FileSystemObject’s OpenTextFile (Refer )
Set oFil = oFS.OpenTextFile("c:\testasc.txt")
and uses the Split Function to convert each line to an array of two elements and iterate through the document
Sub Convert_Symbols2Entities()
Dim MyString
Dim arFindReplace
Dim oFS As Object
On Error GoTo Err_Found
Selection.HomeKey wdStory, wdMove
Set oFS = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set oFil = oFS.OpenTextFile("c:\testasc.txt")
Do Until oFil.AtEndOfStream ' Loop until end of file.
MyString = oFil.ReadLine
' Report if the Input is not Tab Separated
If InStr(1, MyString, Chr(9)) = 0 Then
Open ActiveDocument.Path & "\" & "SymbolsError.txt" For Append As 3
Print #3, MyString & " not replaced"
Close #3
GoTo TakeNext
End If
' Split the Input to Find & Replace Text
arFindReplace = Split(MyString, Chr(9))
' Report if ASCII Value is not valid
If Val(arFindReplace(0)) = 0) Then '' Then
Open ActiveDocument.Path & "\" & "SymbolsError.txt" For Append As 3
Print #3, MyString & " ASCII Value not valid"
Close #3
GoTo TakeNext
End If
Selection.Find.ClearFormatting
Selection.HomeKey wdStory, wdMove
With Selection.Find
.Text = ChrW(Val(arFindReplace(0)))
.Replacement.Text = arFindReplace(1)
End With
Selection.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
TakeNext:
Loop
LastCommands:
Close #1 ' Close file.
If Not oFS Is Nothing Then Set oFS = Nothing
Exit Sub
Err_Found:
' ----------------------------
' Error Handling
' ----------------------------
If Err <> 0 Then
Debug.Assert Err.Number <> 0
MsgBox Err.Number & " " & Err.Description & " has occurred", vbCritical, "ASCII Convert"
Err.Clear
GoTo LastCommands
End If
The code uses ChrW function, which returns a String containing the Unicode character except on platforms where Unicode is not supported
 Word Document Properties
Word Document Properties Word Advanced Properties
Word Advanced Properties Word Quick Parts Dialog
Word Quick Parts Dialog Insert DocProperty in Word Document
Insert DocProperty in Word Document Word DocProperty Field
Word DocProperty Field