Thursday, April 17, 2008
Check If Workbook is Saved using Excel VBA
Use Saved property of Workbook to check the status. Saved returns True if no changes have been made to the specified workbook since it was last saved
Function IsDirty(ByRef OWB As Workbook) As Boolean
If OWB.Saved = False Then
IsDirty = True
End If
End Function
At times, the workbook would have been created and never saved. In that case, you can use the Path property to identify if it was saved at all
Function IsNeverSaved(ByRef OWB As Workbook) As Boolean
If OWB.Path = "" Then
IsNeverSaved = True
End If
End Function
See also :
Excel VBA - 1004 -- The file could not be accessed
Save and Reopen all Workbooks (Excel VBA)
Save copy of the workbook
SaveAs Dialog - Controlled Save
Save RTF document as word
Set No Of Sheets in a Workbook using Excel VBA
There are many times when you need more than three sheets in a workbook. But when you use Workbooks.Add, it creates a New Workbook with three sheets (default for Microsoft Excel). Later you will add (or delete) the sheets for your use.
Here is another way to solve the problem. Use the Application's SheetsInNewWorkbook property to set the default no. of worksheets
Sub Set_No_Of_Sheets()
' -----------------------------------------
' coded for vbadud.blogspot.com by shasur
' -----------------------------------------
MsgBox "No of sheets in a blank workbook is : " & Application.SheetsInNewWorkbook
' set the Workbook for One Sheet
Application.SheetsInNewWorkbook = 1
' Workbook with only one sheet will be added
Workbooks.Add
' Reset the Workbook for Five Sheets
Application.SheetsInNewWorkbook = 3
End Sub
Here is a way suggested by Jon Peltier, Microsoft Excel MVP (http://PeltierTech.com)
Workbooks.Add([Template])
Template is optional, but if you use one of these constants, it creates a workbook with a single sheet of the type defined by the contant: Many thanks Jon for your suggestion
Many thanks Jon for your valuable suggestion
xlWBATChart, xlWBATExcel4IntlMacroSheet, xlWBATExcel4MacroSheet, or
xlWBATWorksheet
This command then creates a workbook with a single worksheet:
Workbooks.Add xlWBATWorksheet
Check Out-Of-Office Status in Outlook using VBA
Checking out of office status using VBA can be done using PropertyAccessor. The following code uses PropertyAccessor to extract the information
Unlike NamedProperties, PropertyAccessor uses Schema to get the property
Sub Check_Out_Of_Office()
Dim oNS As Outlook.NameSpace
Dim oStores As Outlook.Stores
Dim oStr As Outlook.Store
Dim oPrp As Outlook.PropertyAccessor
Set oNS = Application.GetNamespace("MAPI")
Set oStores = oNS.Stores
For Each oStr In oStores
If oStr.ExchangeStoreType = olPrimaryExchangeMailbox Then
Set oPrp = oStr.PropertyAccessor
MsgBox oPrp.GetProperty("http://schemas.microsoft.com/mapi/proptag/0x661D000B")
End If
Next
End Sub
The PropertyPage object is an abstract object. That is, the PropertyPage object in the Microsoft Outlook Object Library contains no implementation code. Instead, it is provided as a template to help you implement the object in Microsoft Visual Basic. This provides a predefined set of interfaces that Outlook can use to determine whether your custom property page has changed and to notify your program that the user has clicked the Apply or OK button. (If your custom property page does not rely on the Apply button, then you do not need to implement the PropertyPage object.)
A custom property page is an ActiveX control that is displayed by Outlook in the Options dialog box or in the folder Properties dialog box when the user clicks on the custom property page’s tab.
Extract Subject and Body of eMail through Outlook VBA
Many automation revolves around mails; you may want to trigger some process once a mail arrives in the InBox. The following code will help you extract the subject and body content of all mails in InBox
Sub Extract_Body_Subject_From_Mails()
Dim oNS As Outlook.NameSpace
Dim oFld As Outlook.Folder
Dim oMails As Outlook.Items
Dim oMailItem As Outlook.MailItem
Dim oProp As Outlook.PropertyPage
Dim sSubject As String
Dim sBody
On Error GoTo Err_OL
Set oNS = Application.GetNamespace("MAPI")
Set oFld = oNS.GetDefaultFolder(olFolderInbox)
Set oMails = oFld.Items
For Each oMailItem In oMails
sBody = oMailItem.Body
sSubject = oMailItem.Subject 'This property corresponds to the MAPI property PR_SUBJECT. The Subject property is the default property for Outlook items.
Next
Exit Sub
Err_OL:
If Err <> 0 Then
MsgBox Err.Number & " - " & Err.Description
Err.Clear
Resume Next
End If
End Sub
The Subject property is the default property for Outlook items.
Check Outlook Drafts folder for messages using Outlook VBA
Sub Check_Drafts_Folder()
Dim oNS As Outlook.NameSpace
Dim oFld As Outlook.Folder
Dim oItems As Outlook.Items
On Error GoTo OL_Error
Set oNS = Application.GetNamespace("MAPI")
Set oFld = oNS.GetDefaultFolder(olFolderDrafts)
Set oItems = oFld.Items
If oItems.Count <> 0 Then
MsgBox "There are some messages in the draft"
End If
Exit Sub
OL_Error:
MsgBox Err.Description
Err.Clear
End Sub
The program uses the MAPI Namespace and Draft DefaultFolder.
The only supported name space type is "MAPI". The GetNameSpace method is functionally equivalent to the Session property, which was introduced in Microsoft Outlook 98.
A Folder object that represents the default folder of the requested type for the current profile. If the default folder of the requested type does not exist, for example, because olFolderManagedEmail is specified as the FolderType but the Managed Folders group has not been deployed, then GetDefaultFolder will return Null (Nothing in Visual Basic).
Friday, April 11, 2008
Disable Drag & Drop of Cells in Excel VBA
Sub Disable_Cell_Drag_Drop()
Application.CellDragAndDrop = False
End Sub
Application.CellDragAndDrop = True enables drag & drop
Get Shared Name of a Drive using FileSystemObject
Here is a simple function, which uses FileSystemObject's ShareName function to get the shared name of the drive
Public Function ConvertDrive2ServerName(ByVal sFullPath As String) As String
' --- Replaces the DriveName with ShareName in a given string
Dim FSO As FileSystemObject
Dim sDrive As String
Dim drvName As Drive
Dim sShare As String
On Error GoTo Err_Trap
Set FSO = New FileSystemObject
sDrive = FSO.GetDriveName(sFullPath)
Set drvName = FSO.GetDrive(sDrive)
sShare = drvName.ShareName
If LenB(sShare) <> 0 Then
ConvertDrive2ServerName = Replace(sFullPath, sDrive, sShare, 1, 1, vbTextCompare)
Else
ConvertDrive2ServerName = sFullPath
End If
If Not FSO Is Nothing Then Set FSO = Nothing
' ---------------------------------------
' Error Handling
' ---------------------------------------
Err_Trap:
If Err <> 0 Then
Err.Clear
Resume Next
End If
End Function
Get Device Name using QueryDosDeviceW
ByVal lpDeviceName As Long, _
ByVal lpTargetPath As Long, _
ByVal ucchMax As Long _
) As Long
Const MAX_PATH = 260
Public Function GetNtDeviceName( _
ByVal sDrive As String) As String
Dim bDrive() As Byte
Dim bResult() As Byte
Dim lR As Long
Dim sDeviceName As String
If Right(sDrive, 1) = "\" Then
If Len(sDrive) > 1 Then
sDrive = Left(sDrive, Len(sDrive) - 1)
End If
End If
bDrive = sDrive
ReDim Preserve bDrive(0 To UBound(bDrive) + 2) As Byte
ReDim bResult(0 To MAX_PATH * 2 + 1) As Byte
lR = QueryDosDeviceW(VarPtr(bDrive(0)), VarPtr(bResult(0)), MAX_PATH)
If (lR > 2) Then
sDeviceName = bResult
sDeviceName = Left(sDeviceName, lR - 2)
GetNtDeviceName = sDeviceName
End If
End Function
Sub Trial()
MsgBox GetNtDeviceName("p:")
End Sub
Check Protection of VBA project using Excel VBA
Returns a value indicating the state of protection of a project.
Sub Is_Project_Protected()
If Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.Protection = vbext_pp_locked Then
MsgBox "Protected"
End If
End Sub
Check Default Reference using Excel VBA
Sub If_Reference_Is_Default()
Dim i1
For i1 = 1 To Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References.Count
'Returns a Boolean value indicating whether or not the reference is a default reference that can't be removed.
If Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References(i1).BuiltIn = True Then
MsgBox "Default Reference : " & Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References(i1).name
Else
MsgBox "Not Default Reference : " & Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References(i1).name
End If
Next i1
End Sub
Get References of VBA Project Programmtically
The References property returns the set of references in a project. It is an accessor property (that is, a property that returns an object of the same type as the property name).
Sub Get_References_in_Project()
Dim i1
For i1 = 1 To Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References.Count
' Get the Name of the Reference
RefName = Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References(i1).name
' Get the Description of Reference
RefDesc = Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References(i1).Description
'Returns a Boolean value indicating whether or not the Reference object points to a valid reference in the registry. Read-only.
If Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References(i1).IsBroken = True Then
RefBroken = True
End If
Next i1
End Sub
Set VBProject Properties using VBA
The ActiveVBProject property returns the project that is selected in the Project window or the project in which the components are selected. In the latter case, the project itself isn't necessarily selected. Whether or not the project is explicitly selected, there is always an active project. This name, description of the VB Project can be set as follows:
Sub Get_The_PRoject_Name()Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.name = "MyVBAProject"
Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.Description = "This is My Personal VBA Project"
End Sub
Scroll to a position in Excel using VBA
Application.GoTo can be used to scroll to a specific location in Excel sheet. Application.GoTo selects any range or Visual Basic procedure in any workbook, and activates that workbook if it’s not already active.
Sub Scroll_To_A_Location()
Application.GoTo Sheets(3).Range("A200"), True
End Sub
This method differs from the Select method in the following ways:
If you specify a range on a sheet that’s not on top, Microsoft Excel will switch to that sheet before selecting. (If you use Select with a range on a sheet that’s not on top, the range will be selected but the sheet won’t be activated).
This method has a Scroll argument that lets you scroll through the destination window.
When you use the Goto method, the previous selection (before the Goto method runs) is added to the array of previous selections. You can use this feature to quickly jump between as many as four selections.
The Select method has a Replace argument; the Goto method doesn’t.
Hide Excel Status Bar / Show Excel Status Bar using VBA
Here is the simple way to hide/show the status bar in Excel
Sub Hide_Status_Bar()
Application.DisplayStatusBar = False
End Sub
Sub Show_Status_Bar()
Application.DisplayStatusBar = True
End Sub
Also you need to clear the contents of the status bar.
Sub Clear_Status_Bar()
Application.StatusBar = False
(or)
Application.StatusBar = ""
End Sub
Retrieving Special Folders using FileSystemObject
Sub Get_Special_Folders()
' Uses File System Object
' Need to have reference to Microsoft Scripting Runtime
On Error GoTo Show_Err
Dim oFS As FileSystemObject
Dim sSystemFolder As String
Dim sTempFolder As String
Dim sWindowsFolder As String
Set oFS = New FileSystemObject
' System Folder - Windows\System32
sSystemFolder = oFS.GetSpecialFolder(SystemFolder)
' Temporary Folder Path
sTempFolder = oFS.GetSpecialFolder(TemporaryFolder)
' Windows Folder Path
sWindowsFolder = oFS.GetSpecialFolder(WindowsFolder)
If Not oFS Is Nothing Then Set oFS = Nothing
Show_Err:
If Err <> 0 Then
MsgBox Err.Number & " - " & Err.Description
Err.Clear
End If
End Sub
For this you need to reference Microsoft Scripting Runtime
See also:
How to retrieve Application Data Folder using C# (.NET)
How to get the full path of cookies folder using C# (.NET)
Selecting a Folder in VB.Net
How to retrieve MyDocuments Folder using C# (.NET)
How to retrieve Desktop Folder using C# (.NET)
Monday, March 31, 2008
Identify End of Document using Word VBA
Most often when we loop through the document, we need to know the End of Word Document. We can achieve that by using Bookmarks
Sub Drive_IS_EOD()
If IS_EOD(Selection.Range) = True Then
MsgBox "End of Document"
Else
MsgBox "Miles to Go:)"
End If
End Sub
The function below uses the Exists method to check if the bookmark exist in the specified range
Function IS_EOD(ByRef MRange As Range) As Boolean
If MRange.Bookmarks.Exists("\EndOfDoc") = True Then
IS_EOD = True
End If
End Function
\EndOfDoc is a predefined bookmark, which is used here
Check Existence of BookMark using VBA (Word VBA)
BookMarks are vital in Word. However, when you look for a particular bookmark using VBA, it will cease to exist causing 5101 - This bookmark does not exist error.
To avoid this it is better to use Exists Method to check if the Bookmark exist.
Sub Check_If_BookMark_Exists()
If ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Exists("TempBKMK") = True Then
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks("TempBKMK").Range.Text = "Something"
End If
End Sub
Exists method determines whether the specified bookmark or task exists. Returns True if the bookmark or task exists
Adding Images to Header using VBA (Word VBA)
Most often we will be using company's logo in Header. Here is the way to do it using VBA
Sub Add_File_Header()
Set docActive = Word.ActiveDocument
ActiveDocument.Sections(1).Headers(wdHeaderFooterPrimary).Range.InlineShapes.AddPicture "C:\My Documents\My Pictures\MYPicture.bmp"
docActive.ActiveWindow.ActivePane.View.SeekView = wdSeekCurrentPageHeader
ActiveDocument.Sections(1).Headers(wdHeaderFooterPrimary).Range.Text = "Header text" ' ERROR
objWord.ActiveDocument.ActiveWindow.View.SeekView = wdSeekMainDocument
With docActive.PageSetup
.DifferentFirstPageHeaderFooter = False 'Set this to false will put text on first page, else will not.
End With
End Sub
Updating Word Fields (VBA)
Here is a simple macro that will update all the fields in a Word document
Sub Update_Field()
ActiveWindow.ActivePane.View.Type = wdPrintView
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Selection.WholeStory
ActiveDocument.Fields.Update
End Sub
Sunday, March 02, 2008
Save and Reopen all Workbooks (Excel VBA)
Use SaveWorkspace method to save the current workspace and use the Open method to open the files again
Sub WorkPlace_Save_And_Resume()
' Save Workspace
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Application.SaveWorkspace "C:\New Folder\TempWorkSpace.XLW"
Workbooks.Close
' Do my work here without anyother workbooks
Workbooks.Open "C:\New Folder\TempWorkSpace.XLW"
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End Sub
The files in the application will be saved and re-opened using Open method
See also :
Excel VBA - 1004 -- The file could not be accessed
Save and Reopen all Workbooks (Excel VBA)
Save copy of the workbook
SaveAs Dialog - Controlled Save
Save RTF document as word
Run a Macro from Different Workbook
Runs a macro or calls a function. This can be used to run a macro written in Visual Basic or the Microsoft Excel macro language, or to run a function in a DLL or XLL.
Sub Run_Macro_In_Different_WorkBook()
Application.Run "'C:\CanBeDeleted.xlsx.xlsm'!AnotherWrkBook_Macro"
End Sub
Runs a macro or calls a function. This can be used to run a macro written in Visual Basic or the Microsoft Excel macro language, or to run a function in a DLL or XLL.
Sub Run_Macro_In_Different_WorkBook_With_Arguments()
On Error GoTo Err_Trap
Application.Run "'C:\CanBeDeleted.xlsx.xlsm'!Function_Two_Args", "Argument 1", "Argument 2"
Err_Trap:
If Err <> 0 Then
Debug.Print Err.Number & Err.Description
End If
End Sub
The above code passes arguments to a macro in another workbook
The following errors need to be handled for forward compatibility of your macro
450 - Wrong number of arguments or invalid property assignment
449 - Argument not optional
Find Number of Days in a month using VBA (Excel 2007)
EOMONTH returns the serial number for the last day of the month that is the indicated number of months before or after start_date. Use EOMONTH to calculate maturity dates or due dates that fall on the last day of the month.
Function No_of_Days_in_Month()
Dim WrkMonths As Integer
Dim StartDate As Date
Dim EndDate As Date
StartDate = Now
EndDate = WorksheetFunction.EoMonth(StartDate, 0)
' if you want the days count
MsgBox "No of days in current month := " & Day(EndDate)
End Function
The above code will work only in Excel 2007
Find Last Day of the Month using VBA (Excel 2007)
EOMONTH returns the serial number for the last day of the month that is the indicated number of months before or after start_date. Use EOMONTH to calculate maturity dates or due dates that fall on the last day of the month.
Function Last_Day_Of_the_Month()
Dim WrkMonths As Integer
Dim StartDate As Date
Dim EndDate As Date
StartDate = Now
EndDate = WorksheetFunction.EoMonth(StartDate, 0)
MsgBox "Last day of the current month is := " & EndDate
End Function
The above code will work only in Excel 2007
Calculate End Date of the Project using Excel VBA
EDATE returns the serial number that represents the date that is the indicated number of months before or after a specified date (the start_date). Use EDATE to calculate maturity dates or due dates that fall on the same day of the month as the date of issue.
Function Get_The_EndDate()
Dim WrkMonths As Integer
Dim StartDate As Date
Dim EndDate As Date
StartDate = Now
EndDate = WorksheetFunction.EDate(StartDate, 3)
MsgBox "End Date of the Project is := " & EndDate
End Function
The above will work in Excel 2007 only
Disallow user interaction - Excel VBA
Sub Hold_User_Interaction()
Application.Interactive = False
' Do necessary calculations / processing
Application.Interactive = True
End Sub
Application.Interactive is True if Microsoft Excel is in interactive mode; this property is usually True. If you set the this property to False, Microsoft Excel will block all input from the keyboard and mouse (except input to dialog boxes that are displayed by your code). Blocking user input will prevent the user from interfering with the macro as it moves or activates Microsoft Excel objects. Read/write Boolean.
Remarks
This property is useful if you're using DDE or OLE Automation to communicate with Microsoft Excel from another application.
If you set this property to False, don't forget to set it back to True. Microsoft Excel won't automatically set this property back to True when your macro stops running.
Voice Messages in VBA
If you are developing applications for one and all, it would be great if you broadcast the messages in voice format. Here is the way you can achieve it in Excel VBA 2007
Sub Speak_Out()
Application.Speech.Speak "Speaking out to you..."
' Synchronous Method
For i = 1 To 100
i = i + 1
Next i
Application.Speech.Speak "Synchronous Speak"
Application.Speech.Speak "asynchronous Speak - the following code will be executed, when this statment is executed", True
MsgBox "Wait..."
For i = 1 To 100
i = i + 1
Next i
End Sub
The synchronous message allows the message to be executed and holds subsequent code processing. In asynchronous Speak the code after the Speak statements are executed while the message is spelt out.
VBA Response from Message Boxes
Sub Get_Response_From_MessageBoxes()
Dim Response
Response = MsgBox("With to Continue?", vbYesNo, "Yes or No")
If Response = vbYes Then
MsgBox "Reponse was yes!"
Else
MsgBox "Reponse was no"
End If
Response = MsgBox("Error while processing", vbAbortRetryIgnore, "Abort Retry ignore")
If Response = vbAbort Then
Exit Sub
ElseIf Response = vbRetry Then
GoTo StartAgain
ElseIf Response = vbIgnore Then
'... continue ...
End If
End Sub
Convert Dates to Arrays using Array Function
Here is the way to convert dates to array. Replace the normal quotes used for string to hash (#).
Function Convert_Date_Into_Array()
Dim arDates
arDates = Array(#1/1/2008#, #2/1/2008#, #3/1/2008#)
For i = 1 To UBound(arDates)
MsgBox arDates(i)
Next i
End Function
The Array Function returns a Variant containing an array.
Syntax
Array(arglist)
The required arglist argument is a comma-delimited list of values that are assigned to the elements of the array contained within the Variant. If no arguments are specified, an array of zero length is created.
Exclude Holidays in Net Working Days (Excel VBA)
Many times we are confronted with a situation to estimate the days left in a quarter or year. The catch is the holidays, exclude Christmas, Thanksgiving, Martin Luthers day or Diwali from the working day. Here is a where Excel 2007 has simplified that for us
Returns the number of whole working days between start_date and end_date. Working days exclude weekends and any dates identified in holidays. Use NETWORKDAYS to calculate employee benefits that accrue based on the number of days worked during a specific term.
Here the holidays are excluded from the predefined range.
Function Get_Net_Working_Days_Excluding_Holidays()
Dim WrkDays As Integer
Dim StartDate As Date
Dim EndDate As Date
StartDate = Now
EndDate = #12/12/2008#
WrkDays = WorksheetFunction.NetworkDays(StartDate, EndDate, Range("b2:b15"))
MsgBox "No of Working Days Left := " & WrkDays
End Function
The function is exclusive in Excel 2007. There is no equivalent function in Excel 2003
Dates should be entered by using the DATE function, or as results of other formulas or functions. For example, use DATE(2008,5,23) for the 23rd day of May, 2008. Problems can occur if dates are entered as text
Get Net Working Days in a Year / Quarter using VBA
Many times we are confronted with a situation to estimate the days left in a quarter or year. Here is a where Excel 2007 has simplified that for us
Returns the number of whole working days between start_date and end_date. Working days exclude weekends and any dates identified in holidays. Use NETWORKDAYS to calculate employee benefits that accrue based on the number of days worked during a specific term.
Function Get_Net_Working_Days()
Dim WrkDays As Integer
Dim StartDate As Date
Dim EndDate As Date
StartDate = Now
EndDate = #12/31/2008#
WrkDays = WorksheetFunction.NetworkDays(StartDate, EndDate)
Publish Post
MsgBox "No of Working Days Left := " & WrkDays
End Function
The function is exclusive in Excel 2007. There is no equivalent function in Excel 2003
Sleep Function in Excel VBA
You can use Application.Wait instead of sleep function to hold the process for a specified period of time.
Here is the way to achieve that:
Sub Setting_Sleep_Without_Sleep_Function()
Debug.Print Now
Application.Wait DateAdd("s", 10, Now)
Debug.Print Now
End Sub
The code will give the following output
02-03-2008 19:12:47
02-03-2008 19:12:57
If you still require the Sleep Method here is it for you:
Private Declare Sub Sleep Lib "kernel32" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long)
Here is a classical example of the use of Sleep function in a splash screen
Private Sub Form_Activate()
frmSplash.Show
DoEvents
Sleep 1000
Unload Me
frmProfiles.Show
End Sub
Calculate Working days (Excluding Holdiays) using Excel Function / VBA
Most of the time you want to exclude weekends and holidays in the calculation for workdays, here is the simple way to do that.
This uses WORKDAY WorksheetFunction, which returns a number that represents a date that is the indicated number of working days before or after a date (the starting date). Working days exclude weekends and any dates identified as holidays. Use WORKDAY to exclude weekends or holidays when you calculate invoice due dates, expected delivery times, or the number of days of work performed.
Function Calculate_Workday_With_Holidays_direct Value()
Dim WrkDays As Integer
Dim StartDate As Date
Dim EndDate As Date
Dim arHolidays() As Date
'arHolidays() = Array(#1/1/2008#)
StartDate = Now
EndDate = WorksheetFunction.WorkDay(StartDate, 12, #2/23/2008#)
End Function
The following excludes the holiday dates from the range (Range("b2:b15") here)
Function Calculate_Workday_With_Holidays_As_Range()
Dim WrkDays As Integer
Dim StartDate As Date
Dim EndDate As Date
Dim arHolidays() As Date
'arHolidays() = Array(#1/1/2008#)
StartDate = Now
EndDate = WorksheetFunction.WorkDay(StartDate, 12, Range("b2:b15"))
End Function
The above excludes weekends and calculates the end date of the task based on the no. of days
Calculate the End date programmatically, Code Calculate Workdays - Excel VBA,
Calculate Workdays - Excel VBA
Most of the time you want to exclude weekends in the calculation for workdays, here is the simple way to do that.
This uses WORKDAY WorksheetFunction, which returns a number that represents a date that is the indicated number of working days before or after a date (the starting date). Working days exclude weekends and any dates identified as holidays. Use WORKDAY to exclude weekends or holidays when you calculate invoice due dates, expected delivery times, or the number of days of work performed.
Function Calculate_Workday()
Dim WrkDays As Integer
Dim StartDate As Date
Dim EndDate As Date
StartDate = Now
EndDate = WorksheetFunction.WorkDay(StartDate, 12)
End Function
The above excludes weekends and calculates the end date of the task based on the no. of days
Calculate the End date programmatically, Code Calculate Workdays - Excel VBA,
Delete Comments from Excel Workbook using VBA
Most of the times comments are used for internal purpose. This need not go with the workbbok, here is the way to remove it
Sub Remove_Comments_From_WKBK()
'
' Remove Comments from Excel 2007 Workbook
'
'
ActiveWorkbook.RemoveDocumentInformation (xlRDIComments)
End Sub
If you want the same for Excel 2003 and before here is the code
Sub Remove_Comments_From_WKBK_2003()
'
' Remove Comments from Excel 2003 Workbook
'
'
Dim wks As Worksheet
Dim cmnt As Comment
For Each wks In ActiveWorkbook.Sheets
For Each cmnt In wks.Comments
cmnt.Delete
Next cmnt
Next
End Sub
Tuesday, December 04, 2007
Opening Dynamic Text file in Excel
If you update some Excel frequently, you can keep it as shared and then ask your fellow colleagues to check if often (refresh)
One of the good option is to have them as CSV file and use query table to update it regularly
Sub TXT_QueryTable()
Dim ConnString As String
Dim qt As QueryTable
ConnString = "TEXT;C:\Temp.txt"
Set qt = Worksheets(1).QueryTables.Add(Connection:=ConnString, _
Destination:=Range("B1"))
qt.Refresh
End Sub
The Refresh method causes Microsoft Excel to connect to the query table’s data source, execute the SQL query, and return data to the query table destination range. Until this method is called, the query table doesn’t communicate with the data source.
Query Table with Excel as Data Source
It represents a worksheet table built from data returned from an external data source, such as an SQL server or a Microsoft Access database. The QueryTable object is a member of the QueryTables collection
However, it need to be SQL server or a Microsoft Access database always. You can use CSV file or our fellow Microsoft Excel spreadsheet as a data source for QueryTable
Here is one such example, which extracts data from MS Excel sheet
Sub Excel_QueryTable()
Dim oCn As ADODB.Connection
Dim oRS As ADODB.Recordset
Dim ConnString As String
Dim SQL As String
Dim qt As QueryTable
ConnString = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=c:\SubFile.xls;Extended Properties=Excel 8.0;Persist Security Info=False"
Set oCn = New ADODB.Connection
oCn.ConnectionString = ConnString
oCn.Open
SQL = "Select * from [Sheet1$]"
Set oRS = New ADODB.Recordset
oRS.Source = SQL
oRS.ActiveConnection = oCn
oRS.Open
Set qt = Worksheets(1).QueryTables.Add(Connection:=oRS, _
Destination:=Range("B1"))
qt.Refresh
If oRS.State <> adStateClosed Then
oRS.Close
End If
If Not oRS Is Nothing Then Set oRS = Nothing
If Not oCn Is Nothing Then Set oCn = Nothing
End Sub
Use the Add method to create a new query table and add it to the QueryTables collection.
You can loop through the QueryTables collection and Refresh / Delete Query Tables
If you use the above code for Excel 2010, you need to change the connection string to the following
ConnString = "Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;Data Source=C:\Users\Om\Documents\SubFile.xlsx;Extended Properties=Excel 12.0;Persist Security Info=False"
Else it will thrown an 3706 Provider cannot be found. It may not be properly installed. error
See also:
Opening Comma Separate File (CSV) through ADO
Using Excel as Database using VBA (Excel ADO)
Create Database with ADO / ADO Create Database
ADO connection string for Excel
Combining Text Files using VBA
Multiple utilities are available to split & merge text files. However, here is a simple one my friend uses to merge around 30 ascii files into one
It uses File System Object and you need to add a reference of Microsoft Scripting Runtime
Sub Append_Text_Files()
Dim oFS As FileSystemObject
Dim oFS1 As FileSystemObject
Dim oTS As TextStream
Dim oTS1 As TextStream
Dim vTemp
Set oFS = New FileSystemObject
Set oFS1 = New FileSystemObject
For i1 = 1 To 30
Set oTS = oFS.OpenTextFile("c:\Sheet" & i1 & ".txt", ForReading)
vTemp = oTS.ReadAll
Set oTS1 = oFS.OpenTextFile("c:\CombinedTemp.txt", ForAppending, True)
oTS1.Write (vTemp)
Next i1
End Sub
The code is simple.. it searches for files from Sheet1.txt ...Sheet30.txt and copies the content into one variable. Then it appends the content to CombinedTemp.txt
Open XML File in Excel
Sub Open_XML_File()
Dim oWX As Workbook
Set oWX = Workbooks.OpenXML("c:\sample.xml")
End Sub
Sub Open_XML_File_As_List()
Dim oWX As Workbook
Set oWX = Workbooks.OpenXML(Filename:="c:\sample.xml", LoadOption:=XlXmlLoadOption.xlXmlLoadImportToList)
End Sub
This option will work for Excel 2003 and above
Monday, December 03, 2007
Visual Basic - Special Folders (Temp Folder , System Folder)
Sub Get_Special_Folders()
' Uses File System Object
' Need to have reference to Microsoft Scripting Runtime
On Error GoTo Show_Err
Dim oFS As FileSystemObject
Dim sSystemFolder As String
Dim sTempFolder As String
Dim sWindowsFolder As String
Set oFS = New FileSystemObject
' System Folder - Windows\System32
sSystemFolder = oFS.GetSpecialFolder(SystemFolder)
' Temporary Folder Path
sTempFolder = oFS.GetSpecialFolder(TemporaryFolder)
' Windows Folder Path
sWindowsFolder = oFS.GetSpecialFolder(WindowsFolder)
Dim a
a = oFS.GetFolder("m:\9.3 BulkLoad\BLT1_Base15.6\Reports\08-Nov-2007\Output\")
If Not oFS Is Nothing Then Set oFS = Nothing
Show_Err:
If Err <> 0 Then
MsgBox Err.Number & " - " & Err.Description
Err.Clear
End If
End Sub
You need to have reference to Microsoft Scripting Runtime to execute the above code
Array Dimensioning in Visual Basic
The ReDim statement is used to size or resize a dynamic array that has already been formally declared using a Private, Public, or Dim statement with empty parentheses (without dimension subscripts).
You can use the ReDim statement repeatedly to change the number of elements and dimensions in an array. However, you can't declare an array of one data type and later use ReDim to change the array to another data type, unless the array is contained in a Variant. If the array is contained in a Variant, the type of the elements can be changed using an As type clause, unless you’re using the Preserve keyword, in which case, no changes of data type are permitted.
If you use the Preserve keyword, you can resize only the last array dimension and you can't change the number of dimensions at all. For example, if your array has only one dimension, you can resize that dimension because it is the last and only dimension. However, if your array has two or more dimensions, you can change the size of only the last dimension and still preserve the contents of the array. The following example shows how you can increase the size of the last dimension of a dynamic array without erasing any existing data contained in the array.
Here is an example of Array redimensioningSub Array_Dimensioning()
Dim arPreserved() As Integer ' Preserved Array
Dim arErased() As Integer ' Array without Preserve
ReDim Preserve arPreserved(1, 1)
ReDim arErased(1, 1)
arPreserved(1, 1) = 1
ReDim Preserve arPreserved(1, 2)
arPreserved(1, 2) = 2
ReDim Preserve arPreserved(1, 3)
arPreserved(1, 3) = 3
ReDim Preserve arPreserved(2, 3) ' This statement will throw and error
' whereas the following statement will not as the Array is not preserved (Erased)
ReDim arErased(2, 1)
End Sub
If you use the Preserve keyword, you can resize only the last array dimension and you can't change the number of dimensions at all. For example, if your array has only one dimension, you can resize that dimension because it is the last and only dimension. However, if your array has two or more dimensions, you can change the size of only the last dimension and still preserve the contents of the array. The arPreserved falls under this category. However, arErased you can redimension the array in any dimension, but the contents will be erased with every Redim statement
Comparing two Word Documents using Word VBA
Here is a simple routine, which will compare two Microsoft Word documents and return the status.
Sub IsDocument_Equal()
Dim oDoc1 As Word.Document
Dim oResDoc As Word.Document
' Delete the tables from both the document
' Delete the images from both the document
' Replace Paragraphs etc
Set oDoc1 = ActiveDocument
' comparing Document 1 with New 1.doc
oDoc1.Compare Name:="C:\New 1.doc", CompareTarget:=wdCompareTargetNew, DetectFormatChanges:=True
'This will be the result document
Set oResDoc = ActiveDocument
If oResDoc.Revisions.Count <> 0 Then
'Some changes are done
MsgBox "There are Changes "
Else
MsgBox "No Changes"
End If
End Sub
Convert URLs to Hyperlinks using VBA
Microsoft Word has in-built intelligence to convert the URLs or Web Addresses to Hyperlinks automatically. This functionality is executed when you type some website/email address in word document.
For some reason, if you want to be done on the Word document at a later stage you can do the following:
Sub Make_URLs_as_HyperLinks()
Options.AutoFormatReplaceHyperlinks = True
ActiveDocument.Select
Selection.Range.AutoFormat
Selection.Collapse
Options.AutoFormatReplaceSymbols
End Sub
Warning: I have set only AutoFormatReplaceHyperlinks = True and not set/reset others. You need to check all options as autocorrect/autoformat can cause undesirable changes that might go unnoticed
Run a Automatic Macro in Word Document
There are numerous instances where one stores the word document format as a Microsoft Word template. When the user opens the document (using the template), some macro needs to be executed. This can be achieved by RunAutoMacro Method of Word VBA
Sub Run_Macro_In_WordDocument()
Dim oWD As Word.Document
Set oWD = Documents.Add("c:\dcomdemo\sample.dot")
oWD.RunAutoMacro wdAutoOpen
End Sub
Here a new document is open based on the Sample.dot template and once the document is open the AutoOpen macro is fired
RunAutoMacro Method can be used to execute an auto macro that's stored in the specified document. If the specified auto macro doesn't exist, nothing happens
On the other hand, if a normal macro (not auto open etc) needs to be executed, Run method can be used
Application.Run "Normal.FormatBorders"
Monday, November 19, 2007
Create Database with ADO / ADO Create Database
Programmers who have used DAO will definitely miss the CreateDatabase in ADO. Here is one method to do the same using ADO.
For doing this you need to include the ADO Extensions library in the project reference.

This library consists of classes and methods to handle the Schema related activities like creation of database, table etc
The following code uses the Catalog object of the ADOX to create a new Microsoft Access database
Sub Create_DB_and_Table_Using_ADOX()
Dim oDB As ADOX.Catalog
Dim sDBPAth As String
Dim sConStr As String
Dim oCn As ADODB.Connection
Dim oCM As ADODB.Command
' ------------------------
' Set the Path and Connection String
' ------------------------
sDBPAth = "c:\Temp\MyAccounts.mdb"
sConStr = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & sDBPAth & ";"
' ------------------------
' Create New ADOX Object
' ------------------------
Set oDB = New ADOX.Catalog
oDB.Create sConStr
Set oCn = New ADODB.Connection
oCn.ConnectionString = sConStr
oCn.Open
Set oCM = New ADODB.Command
oCM.ActiveConnection = oCn
oCM.CommandText = "Create Table Users (" & _
"[EmpNo] Decimal(6), " & _
"[EmpName] Text(150), " & _
"[JoinDate] Date " & _
")"
oCM.Execute
' ------------------------
' Release / Destroy Objects
' ------------------------
If Not oCM Is Nothing Then Set oCM = Nothing
If Not oCn Is Nothing Then Set oCn = Nothing
If Not oDB Is Nothing Then Set oDB = Nothing
' ------------------------
' Error Handling
' ------------------------
Err_Handler:
If Err <> 0 Then
Err.Clear
Resume Next
End If
End Sub
Though I used the ADODB Query deliberately to create a Table in the new database, you can try it with the Table object in ADOX
Saturday, October 06, 2007
Excel VBA - FindAll Method
Function FindAll(ByVal sText As String, ByRef oSht As Worksheet, ByRef sRange As String, ByRef arMatches() As String) As Boolean
' --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
' FindAll - To find all instances of the1 given string and return the row numbers.
' If there are not any matches the function will return false
' --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
On Error GoTo Err_Trap
Dim rFnd As Range ' Range Object
Dim iArr As Integer ' Counter for Array
Dim rFirstAddress ' Address of the First Find
' -----------------
' Clear the Array
' -----------------
Erase arMatches
Set rFnd = oSht.Range(sRange).Find(What:=sText, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlPart)
If Not rFnd Is Nothing Then
rFirstAddress = rFnd.Address
Do Until rFnd Is Nothing
iArr = iArr + 1
ReDim Preserve arMatches(iArr)
arMatches(iArr) = rFnd.Address ' rFnd.Row ' Store the Row where the text is found
Set rFnd = oSht.Range(sRange).FindNext(rFnd)
If rFnd.Address = rFirstAddress Then Exit Do ' Do not allow wrapped search
Loop
FindAll = True
Else
' ----------------------
' No Value is Found
' ----------------------
FindAll = False
End If
' -----------------------
' Error Handling
' -----------------------
Err_Trap:
If Err <> 0 Then
MsgBox Err.Number & " " & Err.Description, vbInformation, "Find All"
Err.Clear
FindAll = False
Exit Function
End If
End Function
The functions accepts three input parameters - Text To be searched, Worksheet, Search Range and one output Array parameter
The function searches the occurrence of that particular text in the specified range of the Excel Sheet and returns address(es) of all occurrences. The Search is by default part of Excel Cells and not whole cell
Here is a way to implement the function:
Case I : Get Addresses of all matching cells
Sub Drive_The_FindAll_Function()
' Sample Sub to Drive the Function
Dim arTemp() As String 'Temp Array
Dim bFound As Boolean 'Flag
Dim i1 As Integer 'Array Counter
bFound = FindAll("SampleText", ActiveSheet, "B1:C41", arTemp())
If bFound = True Then
For i1 = 1 To UBound(arTemp)
' The Address Can be used for extracting data
MsgBox arTemp(i1)
Next i1
Else
MsgBox "Search Text Not Found"
End If
End Sub
Case II : Modify Data according to Find
In the example shown below, FindAll function is used to search 'SampleText' in column C and if the text is found a Flag 'X' is set against column D
Sub Fill_Based_on_FindAll()
' For All Matching Values in Second Column
' Add 'X' to Column D
Dim arTemp() As String 'Temp Array
Dim bFound As Boolean 'Flag
Dim i1 As Integer 'Array Counter
bFound = FindAll("SampleText", ActiveSheet, "C:C", arTemp())
If bFound = True Then
For i1 = 1 To UBound(arTemp)
' The Row Number Can be used for extracting data
ActiveSheet.Range(arTemp(i1)).Offset(0, 1).Value = "X"
Next i1
Else
MsgBox "Search Text Not Found"
End If
End Sub
Case III : Get the Number of Occurrences
A simple one though; number of occurrences of the text in particular range
Sub Instances_Based_on_FindAll()
' Get the Number of Instances
Dim arTemp() As String 'Temp Array
Dim bFound As Boolean 'Flag
Dim i1 As Integer 'Array Counter
bFound = FindAll("SampleText", ActiveSheet, "C:C", arTemp())
If bFound = True Then
MsgBox "No of instances : " & UBound(arTemp)
Else
MsgBox "Search Text Not Found"
End If
End Sub
Disabling Macros in a Workbook (Excel VBA)
The following code snippet (Excel 2003) uses Application.FileDialog method to open a Workbook and disables the macros in it:
Sub Open_File_With_Macros_Disabled()
Dim i1 As Integer
Dim secAutomation As MsoAutomationSecurity
secAutomation = Application.AutomationSecurity
Application.AutomationSecurity = msoAutomationSecurityForceDisable
With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogOpen)
.Show
For i1 = 1 To .SelectedItems.Count
MsgBox .SelectedItems(i1)
Workbooks.Open .SelectedItems(i1)
Next i1
End With
Application.AutomationSecurity = secAutomation
End Sub
Thursday, October 04, 2007
Automate Lotus Notes eMail using Visual Basic
The following Visual Basic code will send a Notes e-mail message. The code includes examples of code to include an attachment and to save the sent message, which are both optional and can be removed if desired.
Dim Maildb As Object
Dim MailDoc As Object
Dim Body As Object
Dim Session As Object
'Start a session to notes
Set Session = CreateObject("Lotus.NotesSession")
'This line prompts for password of current ID noted in Notes.INI
Call Session.Initialize
'or use below to supply password of the current ID
'Call Session.Initialize("
'Open the mail database in notes
Set Maildb = Session.GETDATABASE("", "c:\notes\data\mail\mymail.nsf")
If Not Maildb.IsOpen = True Then
Call Maildb.Open
End If
'Create the mail document
Set MailDoc = Maildb.CREATEDOCUMENT
Call MailDoc.ReplaceItemValue("Form", "Memo")
'Set the recipient
Call MailDoc.ReplaceItemValue("SendTo", "John Doe")
'Set subject
Call MailDoc.ReplaceItemValue("Subject", "Subject Text")
'Create and set the Body content
Set Body = MailDoc.CREATERICHTEXTITEM("Body")
Call Body.APPENDTEXT("Body text here")
'Example to create an attachment (optional)
Call Body.ADDNEWLINE(2)
Call Body.EMBEDOBJECT(1454, "", "C:\filename", "Attachment")
'Example to save the message (optional)
MailDoc.SAVEMESSAGEONSEND = True
'Send the document
'Gets the mail to appear in the Sent items folder
Call MailDoc.ReplaceItemValue("PostedDate", Now())
Call MailDoc.SEND(False)
'Clean Up
Set Maildb = Nothing
Set MailDoc = Nothing
Set Body = Nothing
Set Session = Nothing
Note: The Visual Basic programmer needs to set the Reference to use Lotus Domino objects prior to implementing this function. To enable the Lotus Notes classes to appear in the Visual Basic browser, you must execute the following within VB: Select Tools, References and select the checkbox for 'Lotus Notes Automation Classes'.
The above code is from the IBM support. GETDATABASE given here is pointing to the sample MailDB; you need to change that to your DB.
You can do that by
UserName = Session.UserName
MailDbName = Left$(UserName, 1) & Right$(UserName, (Len(UserName) - InStr(1, UserName, " "))) & ".nsf"
'Open the mail database in notes
Set Maildb = Session.GETDATABASE("", MailDbName)
To send it through Microsoft Outlook refer http://vbadud.blogspot.com/2007/04/vba-email-automation-vba-mail.html
Automate Email, VBA Email, Send Email from Excel, VBA Mail automation, Mail Automation, Lotus Notes VBA, Automate Lotus Notes, Send Mail from Lotus Notes, Link Excel with Lotus Notes,Microsoft Lotus Notes Mail Automation, Excel VBA Mail, MAPI, Send Multiple eMails
Wednesday, September 26, 2007
Reducing Size of Microsoft Access Database (Compact Database)
If the DB Size is huge the compact DB utility [Compact & Repair Database (Tools-->Database utilities-->Compact and Repair Database) should reduce the DB Size.
Here is the code for doing the same using VB/VBA (ADO)
Public Sub CompactDB()
'Microsoft Jet and Replication objects
Dim objJE As New JRO.JetEngine, strSource As String, strTarget As String
DoEvents
Busy True
strSource = " "
strTarget = " "
objJE.CompactDatabase "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & strSource & ";", "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & strTarget & ";Jet OLEDB:Engine Type=4;"
Busy False
'Engine type:
'Access 97 = 4
'Access 2000 = 5
End Sub
Saturday, September 15, 2007
Excel VBA - Change Font Color for Part of Text
Sometimes, you need to differentiate some parts of text in an Excel cell. This can be done using formatting those characters.
Here is the way that can be done using VBA using the Characters property
Sub Color_Part_of_Cell()
'Print ActiveCell.Characters.Count
With ActiveCell.Characters(2).Font
.Color = RGB(36, 182, 36)
End With
With ActiveCell.Characters(2, 2).Font
.Color = RGB(36, 182, 36)
End With
With ActiveCell.Characters(, 2).Font
.Color = RGB(36, 182, 36)
End With
End Sub
The output of the above is

Syntax
expression.Characters(Start, Length)
expression Required. An expression that returns an object in the Applies To list.
Start Optional Variant. The first character to be returned. If this argument is either 1 or omitted, this property returns a range of characters starting with the first character.
Length Optional Variant. The number of characters to be returned. If this argument is omitted, this property returns the remainder of the string (everything after the Start character)
The same characters object can be used to make a character Bold / Italic
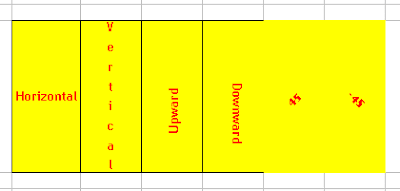
Orientation of Cell Through Excel VBA
Here is an example
Sub Orientations()
ActiveCell.Orientation = xlHorizontal
ActiveCell.Orientation = xlVertical
ActiveCell.Orientation = xlUpward
ActiveCell.Orientation = xlDownward
ActiveCell.Orientation = 45
ActiveCell.Orientation = -45
End Sub
The orientation of the cell in Excel would be as follows:
Tuesday, August 21, 2007
ShutDown Windows using VBA
Option Explicit
' Win API Declarations
Const MF_BYPOSITION = &H400&
Private Const EWX_LOGOFF = 0
Private Const EWX_SHUTDOWN = 1
Private Const EWX_REBOOT = 2
Private Const EWX_FORCE = 4
Private Declare Function ExitWindowsEx Lib "user32.dll" ( _
ByVal uFlags As Long, _
ByVal dwReserved As Long) As Long
Use the function with atmost caution, you will not be warned by Windows for Shutdown / Restart. Save all your work before trying this example:)
Function Common_ShutDown_Logoff()
'Shutdown Windows
Call ExitWindowsEx(EWX_SHUTDOWN, 0)
'Restart Windows
Call ExitWindowsEx(EWX_REBOOT, 0)
'logoff Windows
Call ExitWindowsEx(EWX_LOGOFF, 0)
End Function