Common Dialog not only replaces three controls (Drive, Directory and FileList), but also is easier to program. It is supported in Visual Basic and VBA as well. The new VB.NET has the same functionality in the OpenFileDialog class
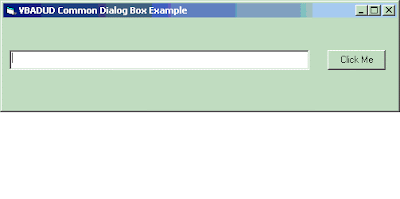
Let us have a small form created for explaining CommonDialog. Let us have a small form with a Text Box and a Command Button. On Clicking the Command Button, the selected file should be displayed in the Text Box
Sample Form:
To use the CommonDialog you need to include the component to your project. You can do so as follows:
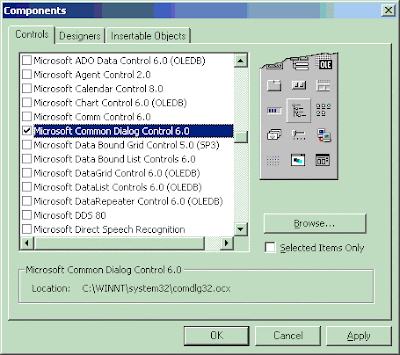
Once The component is included, the CommonDialog will be displayed in the ToolBox
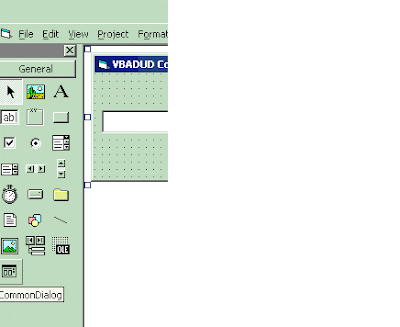
Drag the CommonDialog to the form. You will see a small rectangle there. CommonDialog is visible in the Design time only (it is not visible during runtime)
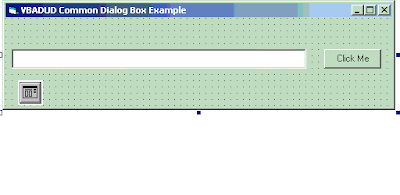
Add the following code to show the CommonDialog box and show the selected file in the text box
Private Sub Command1_Click()
CommonDialog1.DialogTitle = "Select the File..."
CommonDialog1.Flags = cdlOFNFileMustExist
CommonDialog1.Filter = "Microsoft Excel Workbooks (*.xls)*.xls"
CommonDialog1.ShowOpen
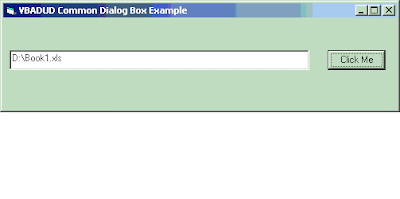
If Len(CommonDialog1.FileName) <> 0 Then
Text1.Text = CommonDialog1.FileName
End If
You can restrict the type of files to be selected using the filter Command. Some common filters are
Selecting Microsoft Word Documents
CommonDialog1.Filter = "Microsoft Word Documents (*.doc)*.docMicrosoft Word Documents (*.rtf)*.rtf"
Selecting Image Files
CommonDialog1.Filter = "Image Files(*.BMP;*.JPG;*.GIF)*.BMP;*.JPG;*.GIF"
Selecting Microsoft Word Documents (Including RTF Files)
CommonDialog1.Filter = "Microsoft Word Documents (*.doc;*.rtf)*.doc;*.rtf"
Selecting Microsoft Excel Workbooks
CommonDialog1.Filter = "Microsoft Excel Workbooks (*.xls)*.xls"
Selecting Excel Addins
CommonDialog1.Filter = "Microsoft Excel Addins (*.xla;*.xll)*.xla;*.xll"
Selecting Any files
CommonDialog1.Filter = "All files (*.*)*.*"
Selecting Text files
CommonDialog1.Filter = "Text files (*.txt)*.txt"
Selecting ASCII files
CommonDialog1.Filter = "ASCII files (*.txt;*.log)*.txt;*.log"
See also:
OpenFileDialog in Visual Basic .Net
Search and Open Files using Excel VBA (FileSearch)
Open Excel Files - Open Dialog - GetOpenFilename Method
Selecting a Folder in VB.Net
Browse a Folder / Select a Folder Thru Shell
SaveAs Dialog - Controlled Save